Being active and exercising is one of the most effective ways to keep your joints healthy. Having said that, injuries happen and they often involve the knee.
Exercise is important and while doing certain stretches, one tends to injure themselves. Wrong form or posture can also lead to injuries.
The knee joint is the largest joint in the human body. It allows movement of the leg and is critical to walking.
Let us understand the basic anatomy of the knee joint and related injuries:
- Bones: The knee joint is made up of 3 bones called the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shinbone) and the patella (knee cap).
- Articular Cartilage: A slippery rubbery substance that covers the joint surface. This cartilage helps the knee bones glide smoothly across each other while moving.
- Meniscus: This is tough and rubbery cartilage between the thigh bone and the shinbone. The meniscus acts as a shock absorber and stabilizes the leg joint.
Injuries
As discussed above, the knee joint is a complex joint which is made up of various components. Any damage to these components may lead to a knee injury.
- Fractures: Any of the knee bones can be fractured due to trauma to the knee joint such as a fall or a car accident. A broken kneecap is the most common fracture of the knee.
- Dislocation: This happens when one of the bones of the knee joint moves out of its place. Traumas, structural abnormalities and contact sports are some of the common causes.
- ACL & PCL injuries: Injuries to the ACL leads to the shinbone translating forward and injuries to the PCL leads to the backwards translation of the shinbone. Contact sports, improper landing from a jump or quickly changing direction while in motion can lead to an ACL injury. A powerful force applied to the knee in a bent position can lead to a PCL injury.
- Meniscal tears: A tear in the meniscus could be sudden due to sporting activity. A meniscus tear can also happen due to ageing.
Treatment
The treatment of a knee injury/pain depends on the cause of the injury. The goal of treatment is to restore stability, strength and mobility. While most knee injuries can be treated non-surgically, a surgical approach may be required for some.
-
R.I.C.E
Rest to minimize the chances of any further injury and help it heal. Icing the muscle reduces blood flow which prevents swelling and pain. Compression prevents fluid build-up which minimizes swelling. It also helps to partially immobilize the knee and ease pain. The elevation is another way to drain out fluid from the injured area and minimize swelling.
-
Rehabilitation Exercises
If the knee pain is not very severe, there are some rehabilitation exercises that can be done to strengthen the muscles around it. These exercises should be done after the swelling has gone down.
- Straight leg raises: Lie down on a flat surface. Bend one knee keeping the other leg extended. Raise the extended leg to a 45-degree angle and back. Repeat in 3 sets of 15. This exercise helps strengthen the quadriceps.
- Hamstring curl: Stand straight holding on to a chair for support. Bend the injured knee and bring the heel of that leg close to your glutes. Hold that position for a couple of seconds. Repeat in 3 sets of 15.
- Prone straight leg raises: Lie down on your stomach with both legs straight. Tighten the muscles around your bottom and raise one leg without bending it to the ceiling. Repeat in 3 sets of 10 on each side.
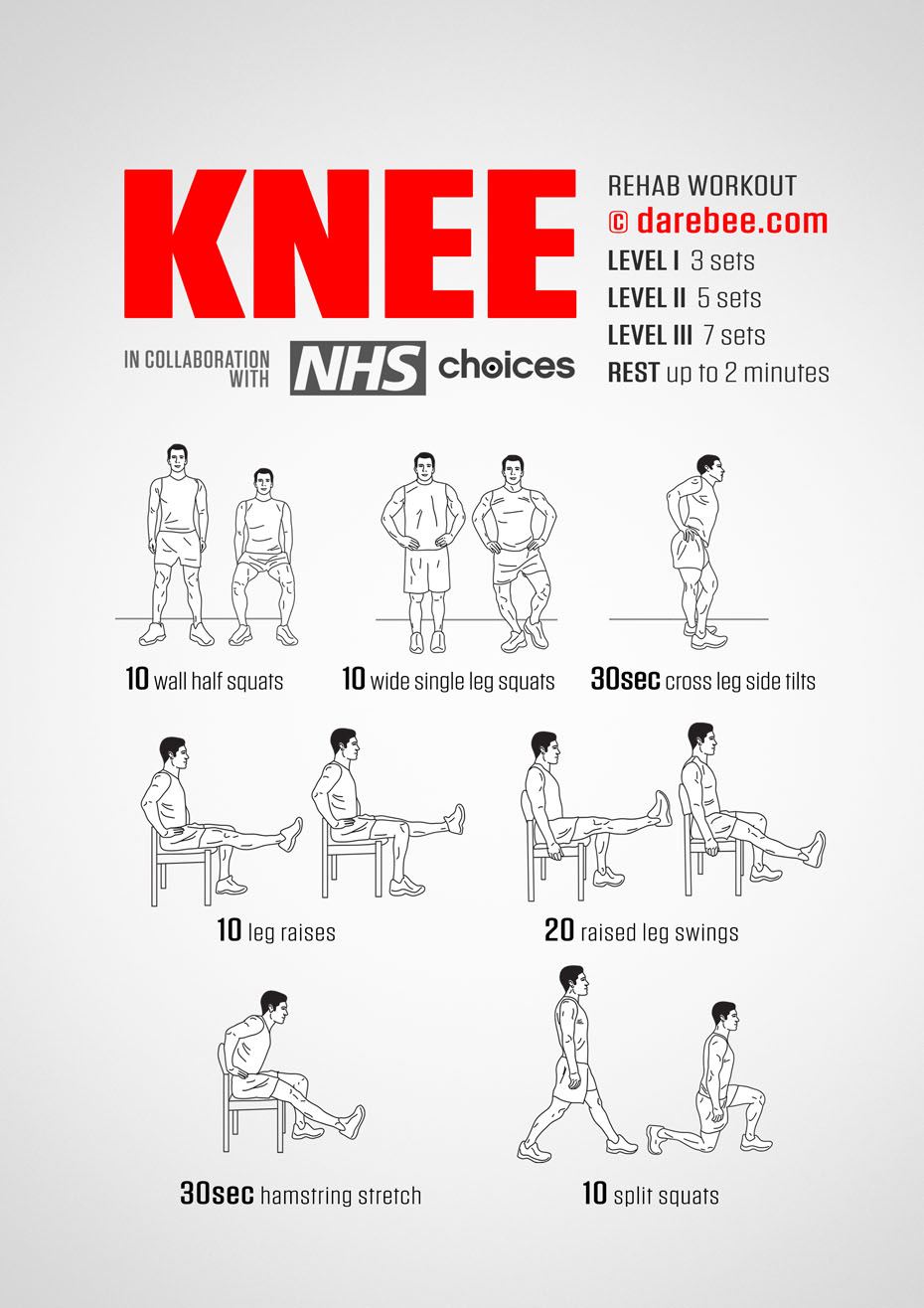
These rehabilitation exercises can also be done post-surgery as directed by the doctor.
- Consult With A Doctor
If there is a trauma to the knee due to direct impact, severe pain or if the pain lasts for more than a week, you should see the doctor.
Following are some of the symptoms to watch out for:
- Inability to stand
- Pain accompanied with noticeable swelling and fever
- Numbness in the affected leg
- Visible signs of injury such as lumps and abnormal appearances
These are some of the ways in which a knee injury can be treated.
However, let’s looks at how we can take some precautionary measures to avoid these injuries/pain:
- Warm up before and after an exercise
- Avoid a sudden increase in the intensity of an exercise.
- Keep the leg muscles strong by exercising them regularly
- Use knee guards in sports where there is a risk of an injury
- Be particular and replace worn out shoes
- Maintain a healthy body weight to avoid added pressure on the knees
Conclusion:
An injured knee can lead to serious inhibitions in functional/daily activities like sitting, standing and walking. Be careful, work towards keeping the leg muscles strong and healthy. In case of an injury, be diligent and follow one of the above steps as required or as suggested by the doctor for an accurate treatment.




